
The F-22 program is developing the next-generation air superiority fighter for the Air Force to counter emerging worldwide threats. It is designed to penetrate enemy airspace and achieve a first-look, first-kill capability against multiple targets. The F-22 is characterized by a low-observable, highly maneuverable airframe; advanced integrated avionics; and aerodynamic performance allowing supersonic cruise without afterburner.
Stealth: Greatly increases survivability and lethality by denying the enemy critical information required to successfully attack the F-22
Integrated Avionics: Allows F-22 pilots unprecedented awareness of enemy forces through the fusion of on- and off-board information
Supercruise: Enhances weapons effectiveness; allows rapid transit through the battlespace; reduces the enemy’s time to counter attack
The F-22's engine is expected to be the first to provide the ability to fly faster than the speed of sound for an extended period of time without the high fuel consumption characteristic of aircraft that use afterburners to achieve supersonic speeds. It is expected to provide high performance and high fuel efficiency at slower speeds as well.
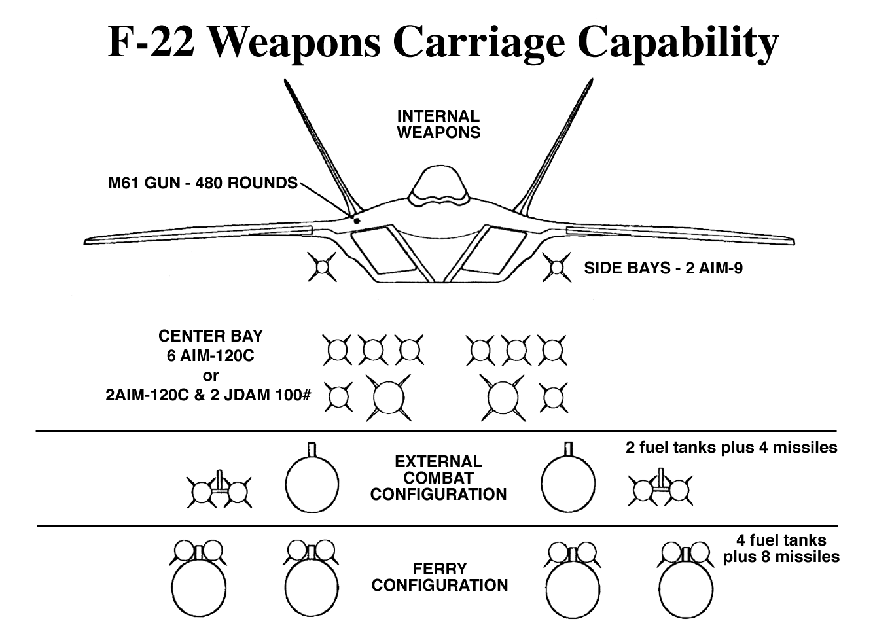
For its primary air-to-air role, the F-22 will carry six AIM-120C and two AIM-9 missiles. For its air-to-ground role, the F-22 can internally carry two 1,000 pound-class Joint Direct Attack Munitions (JDAM), two AIM-120C, and two AIM-9 missiles. With the Global Positioning System-guided JDAM, the F-22 will have an adverse weather capability to supplement the F-117 (and later the Joint Strike Fighter) for air-to-ground missions after achieving air dominance.
The F-22's combat configuration is "clean", that is, with all armament carried internally and with no external stores. This is an important factor in the F-22's stealth characteristics, and it improves the fighter's aerodynamics by dramatically reducing drag, which, in turn, improves the F-22's range. The F-22 has four under wing hardpoints, each capable of carrying 5,000 pounds. A single pylon design, which features forward and aft sway braces, an aft pivot, electrical connections, and fuel and air connections, is used. Either a 600-gallon fuel tank or two LAU-128/A missile launchers can be attached to the bottom of the pylon, depending on the mission. There are two basic external configurations for the F-22:
- Four 600 gallon fuel tanks, no external weapons: This configuration is used when the aircraft is being ferried and extra range is needed. A BRU-47/A rack is used on each pylon to hold the external tanks.
- Two 600 gallon fuel tanks, four missiles: This configuration is used after air dominance in a battle area has been secured, and extra loiter time and firepower is required for Combat Air Patrol (CAP). The external fuel tanks, held by a BRU-47/A rack are carried on the inboard stations, while a pylon fitted with two LAU-128/A rail launchers is fitted to each of the outboard stations.
The F-22 passed milestone II in 1991. At that time, the Air Force planned to acquire 648 F-22 operational aircraft at a cost of $86.6 billion. After the Bottom Up Review, completed by DOD in September 1993, the planned quantity of F-22s was reduced to 442 at an estimated cost of $71.6 billion.
A $9.55 billion contract for Engineering and Manufacturing Development (EMD) of the F-22 was awarded to the industry team of Boeing and Lockheed Martin in August 1991. Contract changes since then have elevated the contract value to approximately $11 billion. Under terms of the contract, the F-22 team will complete the design of the aircraft, produce production tooling for the program, and build and test nine flightworthy and two ground-test aircraft. The F-22 team delivered the final F-22 EMD aircraft to the Air Force in June 2002.
A Joint Estimate Team was chartered in June 1996 to review the F-22 program cost and schedule. JET concluded that the F-22 engineering and manufacturing development program would require additional time and funding to reduce risk before the F-22 enters production. JET estimated that the development cost would increase by about $1.45 billion. Also, JET concluded that F-22 production cost could grow by about $13 billion (from $48 billion to $61 billion) unless offset by various cost avoidance actions. As a result of the JET review the program was restructured, requiring an additional $2.2 billion be added to the EMD budget and 12 months be added to the schedule to ensure the achievement of a producible, affordable design prior to entering production. The program restructure allowed sourcing within F-22 program funds by deleting the three pre-production aircraft and slowing the production ramp. Potential for cost growth in production was contained within current budget estimate through cost reduction initiatives formalized in a government/industry memorandum of agreement. The Defense Acquisition Board principals reviewed the restructured program strategy and on February 11, 1997 the Defense Acquisition Executive issued an Acquisition Defense Memorandum approving the strategy.
The Quadrennial Defense Review Report which was released in mid-May 1997, reduced the F-22 overall production quantity from 438 to 339, slowed the Low Rate Initial Production ramp from 70 to 58, and reduced the maximum production rate from 48 to 36 aircraft per year. The Air Force further slowed the Low Rate Production to 10 aircraft per year in response to GAO recommendations that low rate production not exceed 10 aircraft per year until the Air Force had concluded operational testing and evaluation of the aircraft and certified its operational capability. Initail Operational Testing and Evaluation (IOT&E) is scheduled to be conducted FY 03.
The F-22 EMD program marked a successful first flight on September 7, 1997. The flight test program, which has already begun in Marietta, Georgia, will continue at Edwards AFB, California through the year 2001. Low rate production was initially scheduled to begin in FY99, but restructuring delayed low rate production authorization until August 2001. The Air Force expects to accept delivery of 23 aircraft procured FY 01 - FY 02 during FY 03 - FY 04. Pending aircraft operational tests, the Air Force plans to ramp up procurement starting with FY 2003, to complete delivery by FY 2009. Initial Operational Capability of one operational squadron is slated for December 2005.
The F-15 fleet is experiencing problems with avionics parts obsolescence, and the average age of the fleet will be more than 30 years when the last F-22 is delivered in 2013. But the current inventory of F-15s can be economically maintained in a structurally sound condition until 2015 or later. None of the 918 F-15s that were in the inventory in July 1992 will begin to exceed their expected economic service lives until 2014.
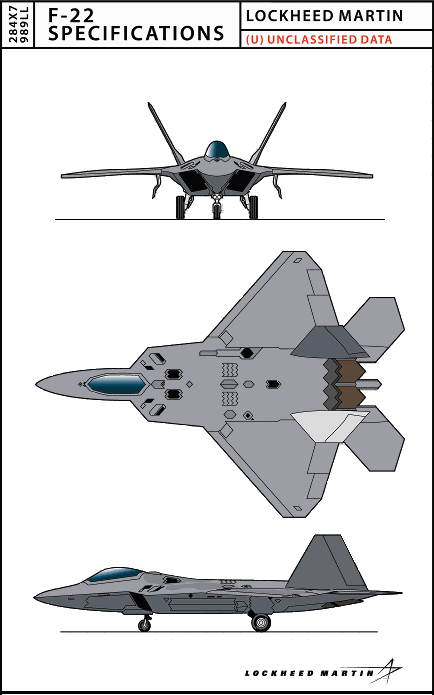
Specifications | |
| Function | Air superiority fighter |
| Contractors |
|
| Major Subcontractors | (partial list): Northrop Grumman, Texas Instruments, Kidde-Graviner Ltd., Allied-Signal Aerospace, Hughes Radar Systems, Harris, Fairchild Defense, GEC Avionics, Lockheed Sanders, Kaiser Electronics, Digital Equipment Corp., Rosemount Aerospace, Curtiss-Wright Flight Systems, Dowty Decoto, EDO Corp., Lear Astronics Corp., Parker-Hannifin Corp., Simmonds Precision, Sterer Engineering, TRW, XAR, Motorola, Hamilton Standard, Sanders/GE Joint Venture, Menasco Aerospace. |
| Propulsion | two Pratt & Whitney F119-PW-100 engines |
| Thrust | 35,000 lbst |
| Length | 62.08 feet, 18.90 meters |
| Height | 16.67 feet, 5.08 meters |
| Wingspan | 44.5 feet, 13.56 meters |
| Wing Area | 840 square feet |
| Horizontal Tailspan | 29 feet, 8.84 meters |
| Maximum Takeoff Weight | |
| Ceiling | |
| Speed | Mach 1.8 (supercruise: Mach 1.5) |
| Crew | one |
| Armament |
|
| First flight: | September 7, 1997 |
| Date Deployed |
deliveries beginning in 2002 operational by 2004 |
| Unit Costs |
DOD's Projected Unit
Prices Before and After Restructuring
Production
--------------------------
Low-rate Full-rate
------------ ------------
Units Unit Units Unit
Estimates cost cost
-------------------------- ---- ------ ---- ------
Before restructuring 76 $142.6 362 $102.8
Restructured without 70 $200.3 368 $128.2
initiatives
Restructured with 70 $200.8 368 $ 92.4
initiatives
------------------------------------------------------
SOURCE: GAO June 1997
|
| VRML 3-D Model |
 F-22 Raptor VRML by Soji Yamakawa |





































No comments:
Post a Comment