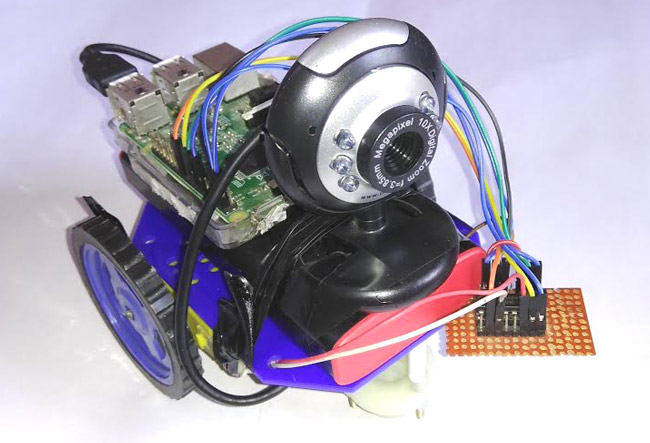
 DIY IoT Based Raspberry Pi Surveillance Robotic Car
DIY IoT Based Raspberry Pi Surveillance Robotic Car
In this DIY session we are building a web controlled surveillance robotic car using raspberry pi and a webcam.
This could be a useful and inexpensive security and spy tool, which
have many configurable options and can be built in few hours. In this IoT Project, we are mainly using Raspberry Pi, USB web camera and two DC motor with Robot chassis to build this Robotic car.
It has a web camera mounted over it, through which
we will get live video feed and the interesting part here is that we
can control and move this robot from a web browser over the internet. As
it can be controlled using webpage, means it can also be controlled
using webpage in Mobile. We built a webpage in HTML which has Left,
Right, Forward, Backward links, clicking on which we can move the robot
in any direction. Here we used “Motion” for getting live Video feed from USB camera and used “Flask” for sending commands from webpage to Raspberry Pi using python
to move the Robot, which are explained in detail in subsequent part of
this tutorial. We have Raspbian Jessie OS installed on our Raspberry Pi
board. You can check this article to install the Raspbian OS and getting started with Raspberry Pi.
Installing and Configuring ‘Motion’ for getting Video feed:
Motion (Surveillance Software) is
free, open source motion detector CCTV software, developed for Linux.
It detects the motion and start recording video of it. With ‘Motion’
installed in your Raspberry Pi, you can magically turn your Raspberry Pi into a Security Camera.
It is used for getting live video feed, making timelapse videos and
taking snapshots at regular interval. It records and saves the Video
whenever it detects Motion or any disturbance in the view area. Live
Video feed can be watched on the web browser by entering the IP address
of Pi along with the port.
We have created a detailed Tutorial on Using Motion with Raspberry Pi and USB Camera, here we are briefly explaining its installing on Raspberry pi for our Robot to send Live video streaming to webpage.
Here you need to run only few commands to start
getting you first video feed over the network. Before that, properly
check that your Raspberry Pi is connected to the internet, either using
LAN or Wi-Fi and then follow below steps:
Step 1: First run the below command to update the Raspbian OS on Raspberry Pi:
sudo apt-get update
Step 2: Then install ‘Motion’ Library by using below command:
sudo apt-get install motion
Step 3: Now set Motion daemon to yes by editing the file: /etc/default/motion so that it will be always running. Edit this file using ‘nano’ editor with ‘sudo’ like given below:
sudo nano /etc/default/motion
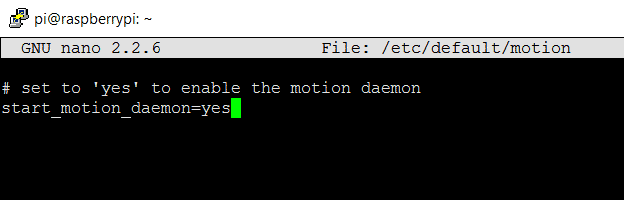
Then save the file by pressing ‘CTRL+X’, then ‘Y’ and the Enter.
Step 4: Now we need to set the permission for the Target Directory (/var/lib/motion/),
in which Motion saves all the Video recordings and picture files. We
need to set ‘Motion’ as owner of this directory by issuing below
command:
sudo chown motion:motion /var/lib/motion/
This permission is necessary otherwise you will get error, when you check Motion service Status.
You can check service status by using this command: sudo service motion status
Step 5: Now we are almost done, only we need to change one config option in Motion configuration file (/etc/motion/motion.conf) which is stream_localhost off. We have to turn off this local host streaming,
otherwise we will not be able to access the Video feed on our network
and it will be only accessible from the Raspberry Pi itself. To doing
so, edit the Motion Configuration file with ‘nano’ editor and turn it
off, like shown below:
sudo nano /etc/motion/motion.conf
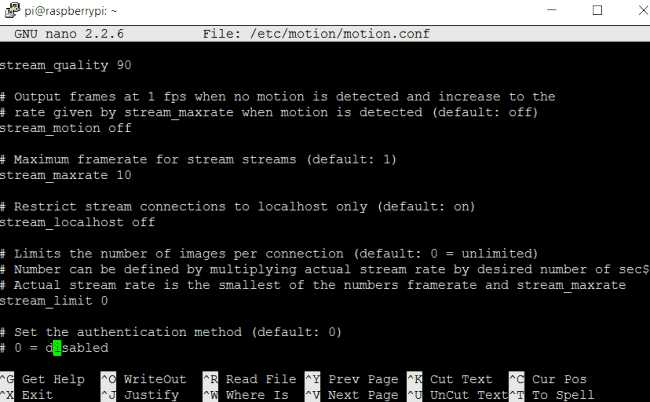
Now we are done and ready to get our live feed
from the USB web camera connected to Pi. Just start (or restart) the
Motion service using below command and open your Raspberry Pi’s IP, with port 8081, in your browser (like 192.168.43.199:8081). In this project we have embed this IP in our HTML code in img src tag.
sudo /etc/init.d/motion restart
And
you will see the live feed from your web camera. Here we have used a
low cost USB web camera which worked smoothly with our Raspberry Pi, but
you can further use a good quality camera for better resolution. As it
will show in browser, you can use any device, to watch the feed, which
supports web browser like Mobile, tablet etc.
Try rebooting the Raspberry Pi as a troubleshooting step when necessary:
sudo reboot
This is all about using Motion for our Surveillance Robot, apart from that, it has several configuration options which we have already discussed in our previous tutorial.
Note: If you are Raspberry Pi model below the version 3, then you may need a Wi-Fi dongle to wirelessly connect raspberry Pi to router.
Flask Setup in Raspberry Pi for Controlling Robot through Webpage:
Here, we have created a web server using Flask, which provides a way to send the commands from webpage to Raspberry Pi to
control the Robot over the network. Flask allows us to run our python
scripts through a webpage and we can send & receive data from
Raspberry Pi to web browser and vice versa. Flask
is a microframework for Python. This tool is Unicode based having
built-in development server and debugger, integrated unit testing
support, support for secure cookies and its easy to use, these things
make it useful for the hobbyist.
Install a flask support package into the Raspberry Pi by using given command:
Then
we can use the Flask by just importing it in our program, like we have
imported following packages of flask for this project:
You can learn more about the programming using Flask here, also check our previous projects where we have used Flask to send the message from Webpage to Raspberry Pi and send weight value to Raspberry Pi in Smart Container.
HTML code for webpage:
We have created a web page using HTML language for
displaying control links (Left, Right, Forward, backward) to move the
Robot from web browser. We have used jQuery script to call the functions in our Python Program. There
are five functions in Python Code to move the Robot Left, Right,
Forward, Backward and to stop it. Complete Python Code has been given at
the end. These functions will be executed by clicking on the Control
Links on webpage and motors will move depending on the link being
clicked. Here we have written the code in such way that Robot will move
in certain direction while clicking and holding the link, and as soon as we release the mouse button Robot will stop. Below is the HTML code for webpage including the jQuery:
Here you can see the we have embed the IP address, on which the Video is streaming, into the webpage by using img src tag. Change the IP address according to your Raspberry Pi but keep the port same.
User
needs to copy-paste the above given HTML code in some text editor
(notepad) and save the file with .HTML extension (robot.html). Then put this HTML file in the /templates folder with respect to your python script location. Means you need to create a folder named templates, where you have put your Python Code file for this Raspberry Surveillance Robot,
then put robot.html file in this templates folder. This step is
important, otherwise our project won’t work. You can directly open the
robot.html file by double clicking on it to see how your control links
will look. Further check the whole process in Demonstration Video at
the end. After we have done with the programming and all, we can just
run the Python code in Raspberry Pi and open
the IP_address_of_your_Pi:5010 in web Browser (like http://192.168.43.199:5010)

You can check the IP address of your Raspberry Pi by using ifconfig command:
ifconfig
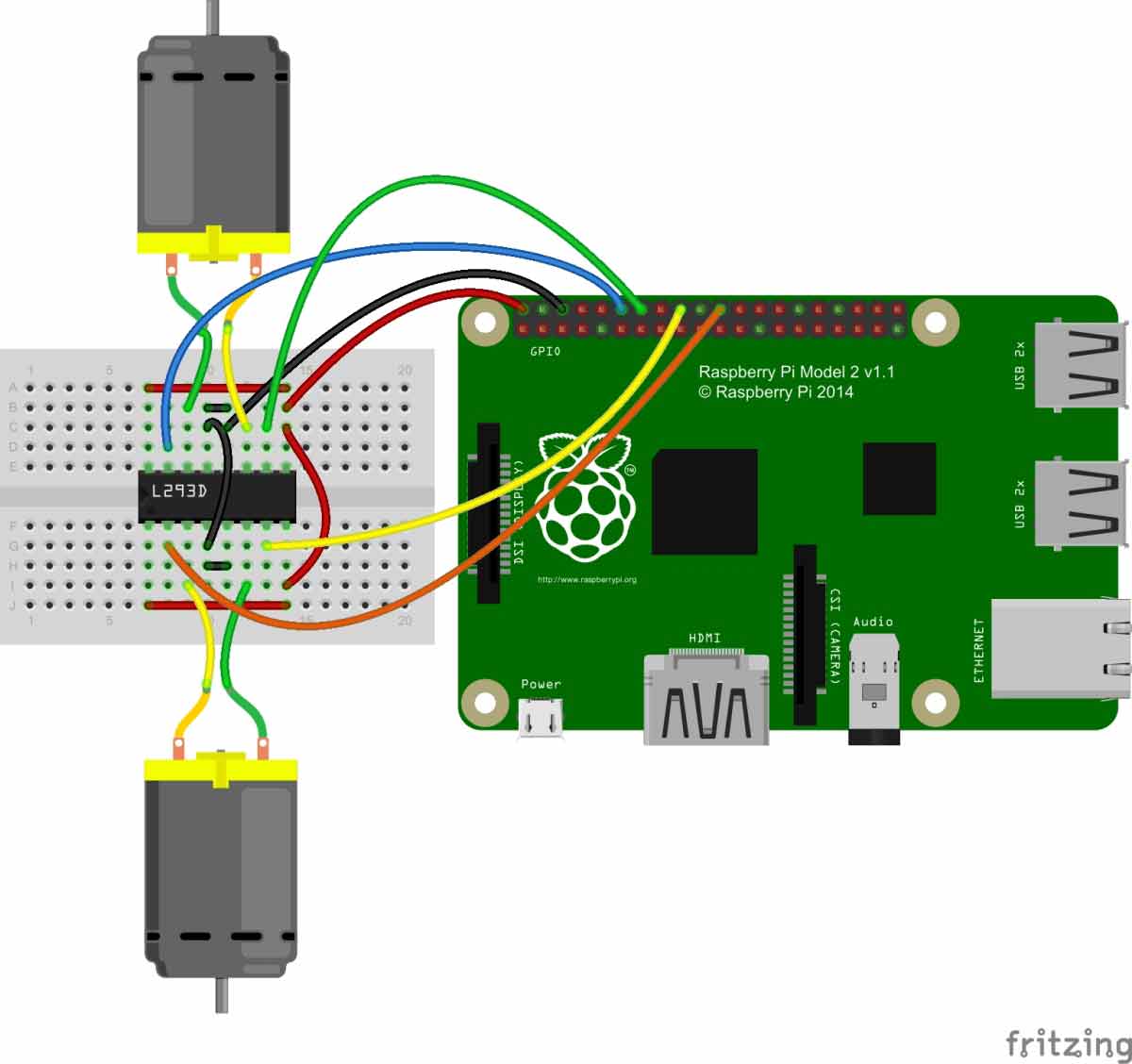
Circuit Diagram and Setup:
After testing the Live Video feed and HTML code,
we need to build a robot by using handmade or ready-made robot chassis,
wheels, and nut-bolts. Then place Power bank over it for powering the
Raspberry pi and then place the Raspberry Pi and web camera over the
power bank and fix the setup using Cello tape or rubber strips, connect
the USB camera with Raspberry Pi.
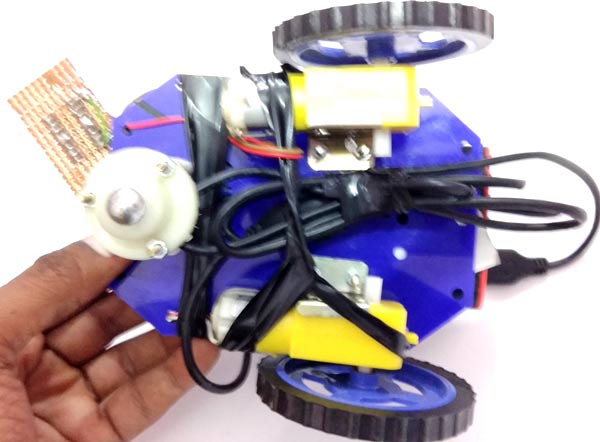
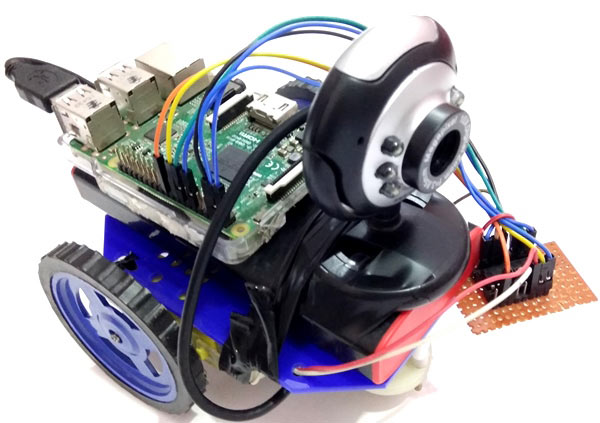

In this IoT project, we don’t need to do many connections, we only need to connect some wires for Motor Driver IC L293D and DC Motors.
Connections are shown in circuit diagram below. Here we have used a
General Purpose PCB for mounting L293D IC to reduce the space but you
can also use small Breadboard for connecting DC motors with L293D.
How to operate:
Operation and Working this Surveillance Robot is
very easy. Create a python file (.py extension) and copy the below code
into it then save it on your Raspberry Pi. Then put the HTML file in the
templates folder as explained above. Don’t forget to change the IP address in HTML file.
Then Run the Python code by entering below command:
Then open your Raspberry Pi IP address with port 5010 like http://192.168.43.199:5010 (again
replace IP address with your address). Now you will see the web page
having four robot control links and live streaming video. User can
control the robot by clicking and holding the links. If user will click
and hold the links then robot will move according to clicked link and
when will user release the link then robot automatically stop.

Complete Python code is given
below, where we have written various functions to control the Robot on
clicking the links on the webpage. You can understand them easily or if
you are a beginner then check our previous Raspberry Pi Tutorials. Also visits our Robotics Section for more interesting and easy to build Robots.
Code:
from flask import Flask
from flask import render_template, request
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
app = Flask(__name__)
m11=18
m12=23
m21=24
m22=25
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(m11, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(m12, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(m21, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(m22, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(m11 , 0)
GPIO.output(m12 , 0)
GPIO.output(m21, 0)
GPIO.output(m22, 0)
print "DOne"
a=1
@app.route("/")
def index():
return render_template('robot.html')
@app.route('/left_side')
def left_side():
data1="LEFT"
GPIO.output(m11 , 0)
GPIO.output(m12 , 0)
GPIO.output(m21 , 1)
GPIO.output(m22 , 0)
return 'true'
@app.route('/right_side')
def right_side():
data1="RIGHT"
GPIO.output(m11 , 1)
GPIO.output(m12 , 0)
GPIO.output(m21 , 0)
GPIO.output(m22 , 0)
return 'true'
@app.route('/up_side')
def up_side():
data1="FORWARD"
GPIO.output(m11 , 1)
GPIO.output(m12 , 0)
GPIO.output(m21 , 1)
GPIO.output(m22 , 0)
return 'true'
@app.route('/down_side')
def down_side():
data1="BACK"
GPIO.output(m11 , 0)
GPIO.output(m12 , 1)
GPIO.output(m21 , 0)
GPIO.output(m22 , 1)
return 'true'
@app.route('/stop')
def stop():
data1="STOP"
GPIO.output(m11 , 0)
GPIO.output(m12 , 0)
GPIO.output(m21 , 0)
GPIO.output(m22 , 0)
return 'true'
if __name__ == "__main__":
print "Start"
app.run(host='0.0.0.0',port=5010)
from flask import render_template, request
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
app = Flask(__name__)
m11=18
m12=23
m21=24
m22=25
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(m11, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(m12, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(m21, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(m22, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(m11 , 0)
GPIO.output(m12 , 0)
GPIO.output(m21, 0)
GPIO.output(m22, 0)
print "DOne"
a=1
@app.route("/")
def index():
return render_template('robot.html')
@app.route('/left_side')
def left_side():
data1="LEFT"
GPIO.output(m11 , 0)
GPIO.output(m12 , 0)
GPIO.output(m21 , 1)
GPIO.output(m22 , 0)
return 'true'
@app.route('/right_side')
def right_side():
data1="RIGHT"
GPIO.output(m11 , 1)
GPIO.output(m12 , 0)
GPIO.output(m21 , 0)
GPIO.output(m22 , 0)
return 'true'
@app.route('/up_side')
def up_side():
data1="FORWARD"
GPIO.output(m11 , 1)
GPIO.output(m12 , 0)
GPIO.output(m21 , 1)
GPIO.output(m22 , 0)
return 'true'
@app.route('/down_side')
def down_side():
data1="BACK"
GPIO.output(m11 , 0)
GPIO.output(m12 , 1)
GPIO.output(m21 , 0)
GPIO.output(m22 , 1)
return 'true'
@app.route('/stop')
def stop():
data1="STOP"
GPIO.output(m11 , 0)
GPIO.output(m12 , 0)
GPIO.output(m21 , 0)
GPIO.output(m22 , 0)
return 'true'
if __name__ == "__main__":
print "Start"
app.run(host='0.0.0.0',port=5010)







No comments:
Post a Comment